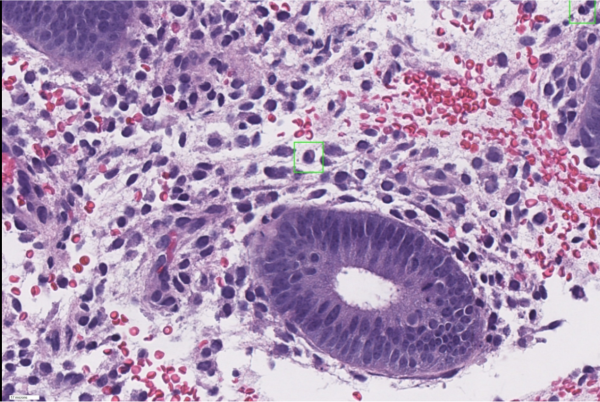
Figure 1: An example of a novel AI detection of diseased cells (in green boxes) in a sample of the tissue lining the uterus.
In the background of the ever changing world, one topic has constantly been dominant: medicine. Because of recent outbreaks such as Covid-19 and new innovations in technology, medicine has become an evolving field. Artificial intelligence (AI) is often touted as the epitome of all things negative such as taking away jobs, limiting human creativity, and more. However, AI has paved the way for more technological innovations across society. One area where AI is making significant strides is in the detection of diseased cells, with the potential to quickly and accurately identify health issues within the human body
New research by Stanford University has changed the AI game in medicine. AI has often been a non-customizable tool with a one size fits all approach. However, in terms of diagnosis, that type of methodology cannot yield the best results. The tool, called nuclei.io, was published on June 19th in the magazine Nature Biomedical Engineering.
The technology was first used to detect diseased colon cancer cells. It has also been used to detect endometriosis, which is an inflammation of the uterine lining. According to the Stanford Medicine News Center, “doctors using nuclei.io were… 62% faster at making diagnoses and 72% more accurate than they were without the program.” In the world of medicine, increasing accuracy of diagnoses in a shorter time frame is critically important to make sure that every human life can be saved.
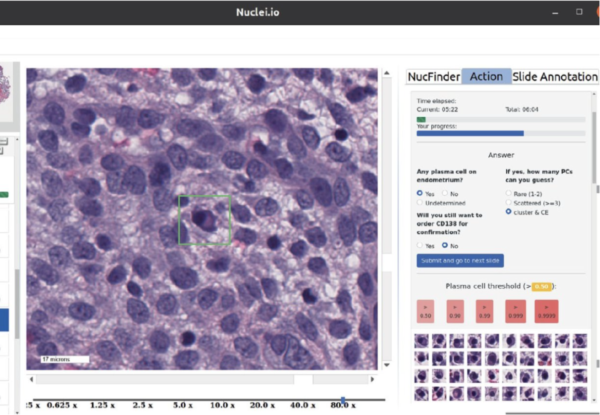
Figure 2: The nuclei.io interface along with the detection process.
“We don’t want a tool that replaces doctors, but something that collaborates well with doctors,” said James Zou, PhD, an associate professor of biomedical data science and the co-senior author of the paper. Zou furthermore states, “we found that a pathologist assisted by the AI is much better than either the pathologist by themselves or the AI by itself.” It’s important to use a dual approach for the maximum benefit of society. The combination of AI and humanity will only open avenues towards a brighter future and start the journey towards the technology we need.
It’s important to note that this is still a novel technology that requires the collaboration of both humans and artificial intelligence. Nuclei.io acts more like a prediction device, giving a general range where the diseased cells are located. Typically, pathologists have to look through hundreds or thousands of cells to try to find a path of infected cells, like trying to find a needle in a haystack. However, according to the Stanford Report, “in less than an hour of use, the AI program learns how to recognize the cells that the individual pathologist wants to look for and highlights those cells on an image.” This technology was able to easily detect the infected cells in a much shorter time frame.
At the end of the day, the primary goal of medicine is to save as many human lives as possible. AI is helping to achieve this goal by offering a sustainable pathway to save human lives by cutting down time and improving accuracy. Nuclei.io is currently underway regulatory approval to open source their data and implement across the Stanford medical system.This development will empower pathologists worldwide to more easily detect diseased cells, revolutionizing biomedicine and computational biology. In doing so, it redefines the impact of AI on the field of biology, paving the way for even greater advancements in healthcare
Works Cited:
“Customizable AI Tool Developed at Stanford Medicine Helps Pathologists Identify Diseased Cells.” StanfordReport, StanfordReport, 19 June 2024, med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2024/06/digital-pathology.html.

